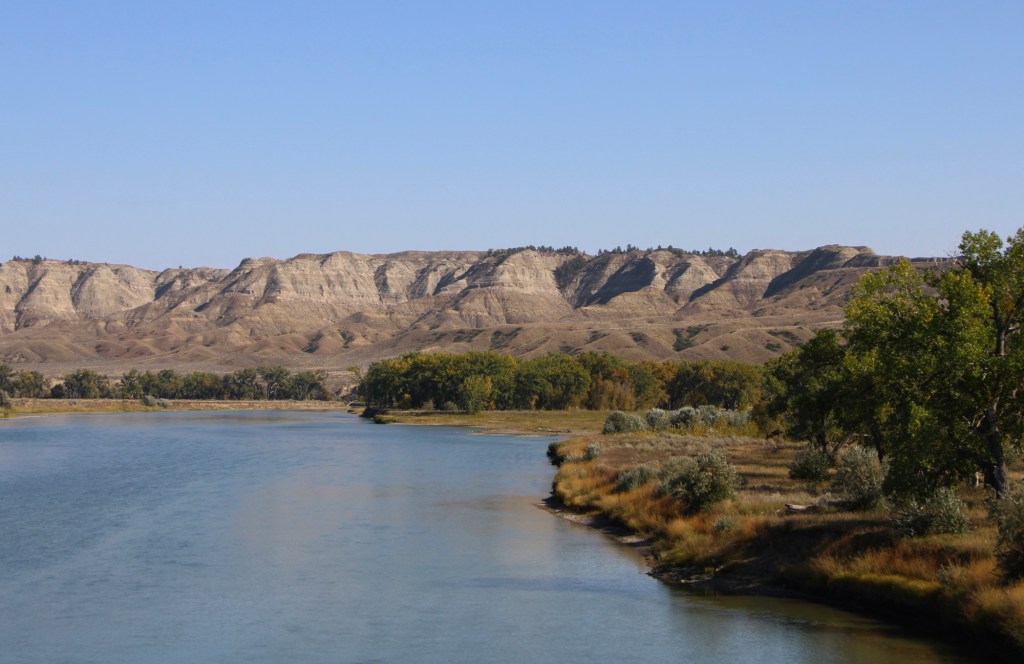
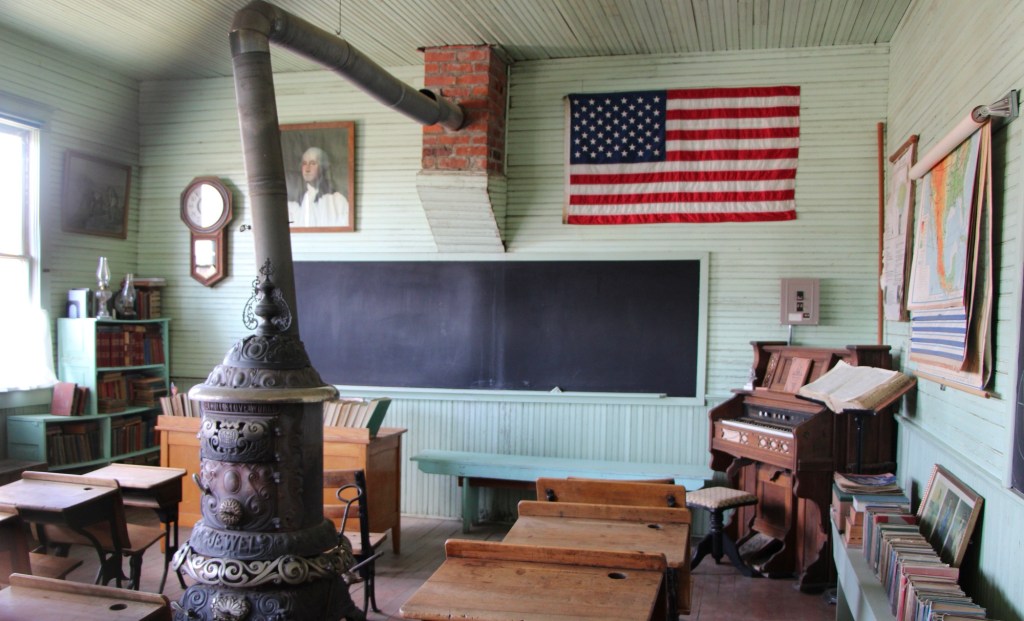
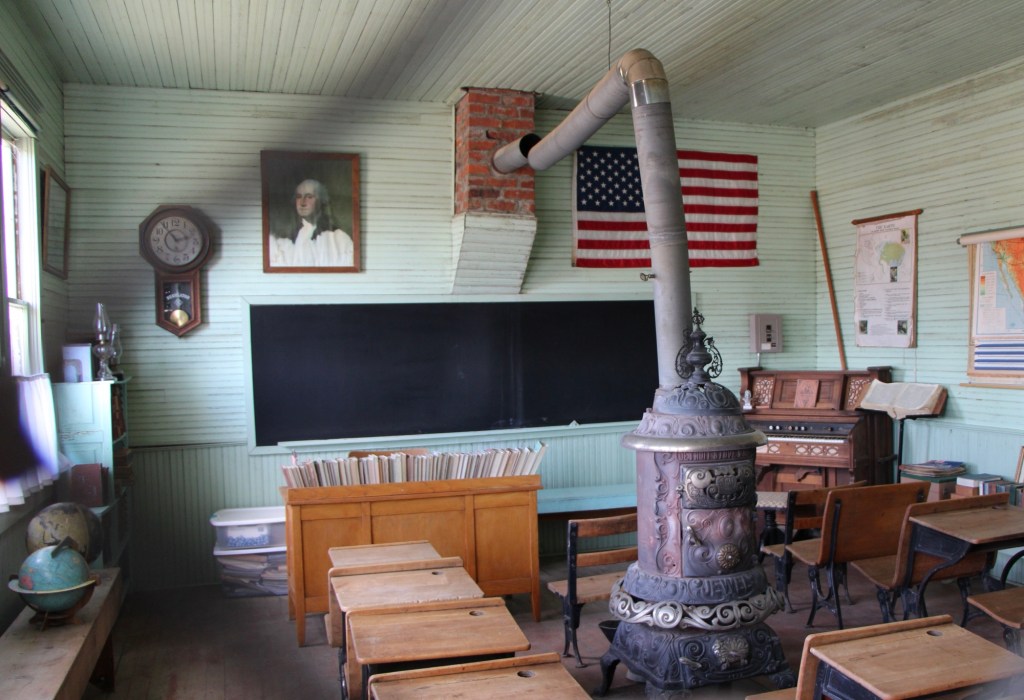
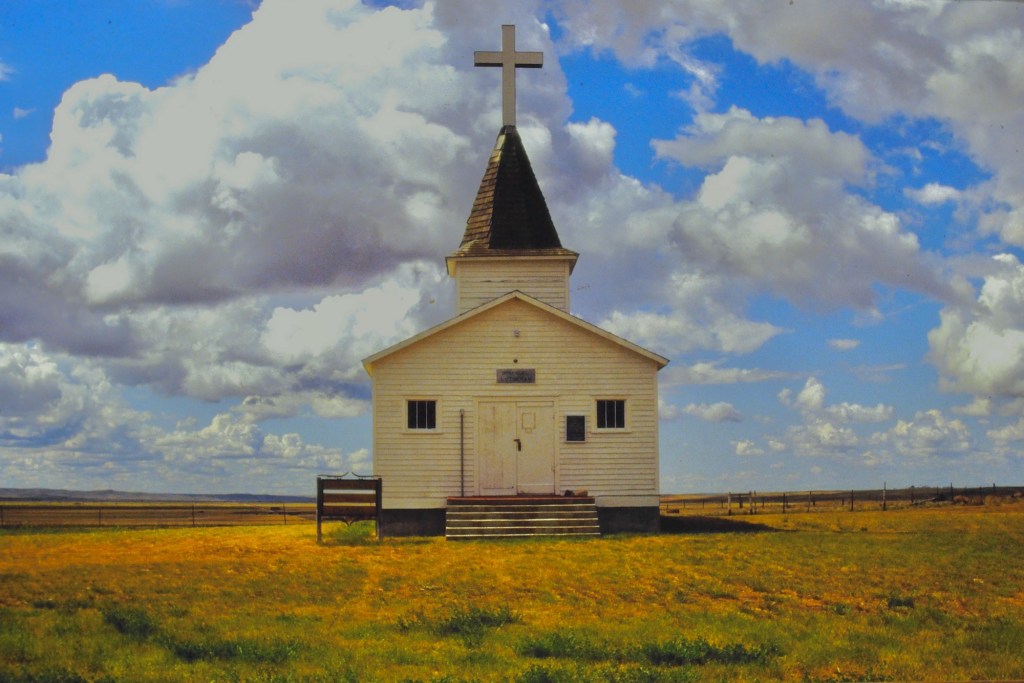
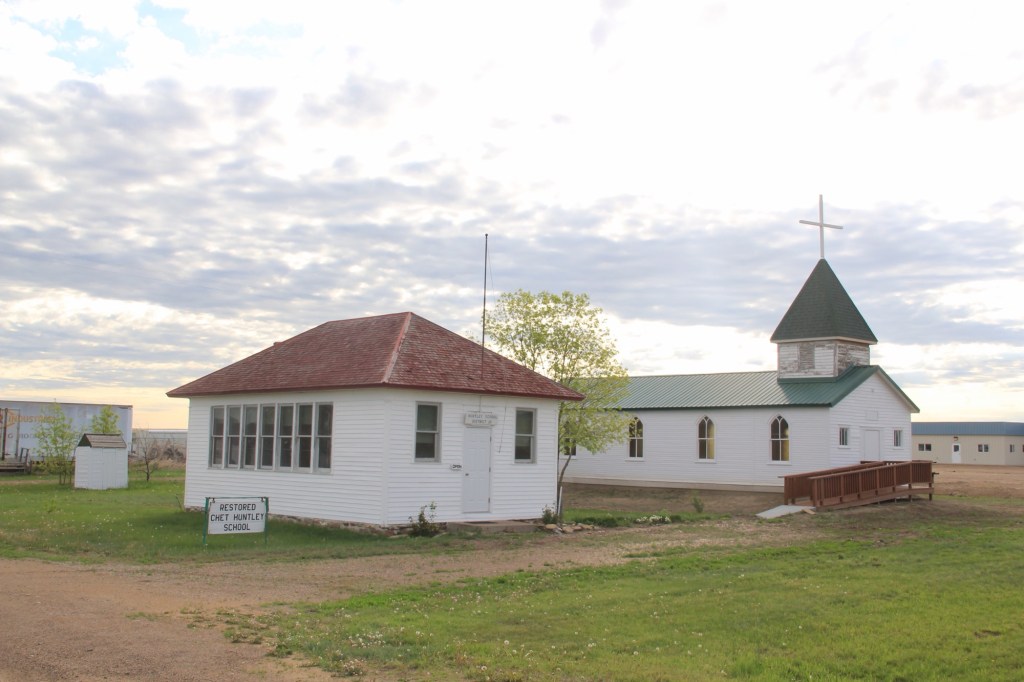
There are few places in the nation more important than the broad river valley at the confluence of the Judith and Missouri rivers in central Montana, a place only accessible by historic gravel roads. When I first visited in 1984, I came from the Fergus County side through Winifred.
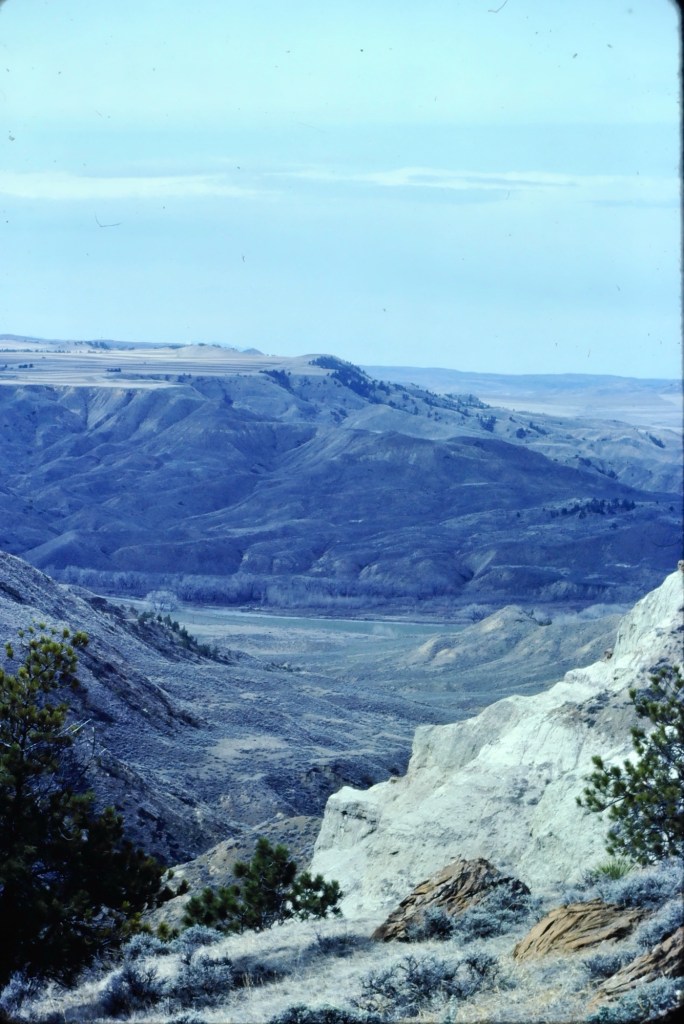

Why is Judith Landing so important? It was a vital and frequently used crossroads for Northern Plains tribes for centuries. Then in 1805 as Lewis and Clark traveled on the Missouri, they camped at the confluence (private property today). In 1844, The American Fur Company established Fort Chardon, a short-lived trading post.

In 1846 Indigenous leaders of several tribes met at Council Island to discuss relations between the Blackfeet and other northwest tribes. In 1855 leaders from the Blackfeet, Salish, Pend d’Oreille, and Nez Perce returned to Council Island to negotiate the Lame Bull treaty, which established communal hunting areas and paved the way for white settlement in the late 1860s and early 1870s.
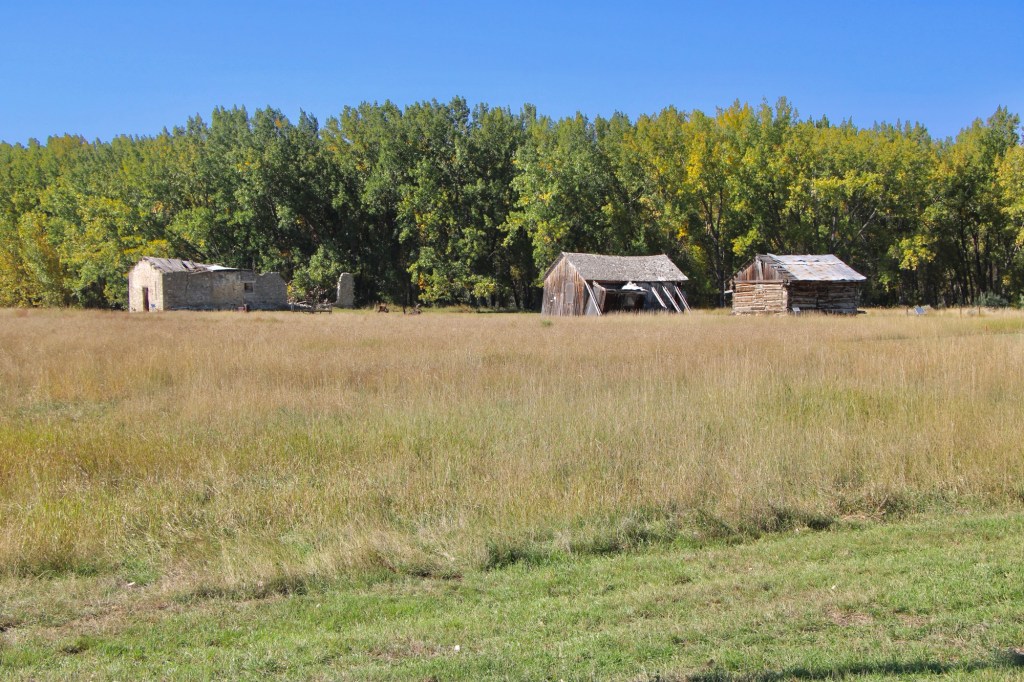

Settlement first came with trading posts, serving a nearby army base, Camp Cooke (1866-1870) and connecting steamboat traffic on the Missouri to nearly mining camps (like Maiden). When the U.S. government moved the base, Fort Benton merchant T.C. Power developed his own businesses and post at Judith Landing and established “Fort Clagett” to the immediate west. In the 1880s he partnered with Gilman Norris to create the famous PN Ranch from the remnants of these early settlement efforts.
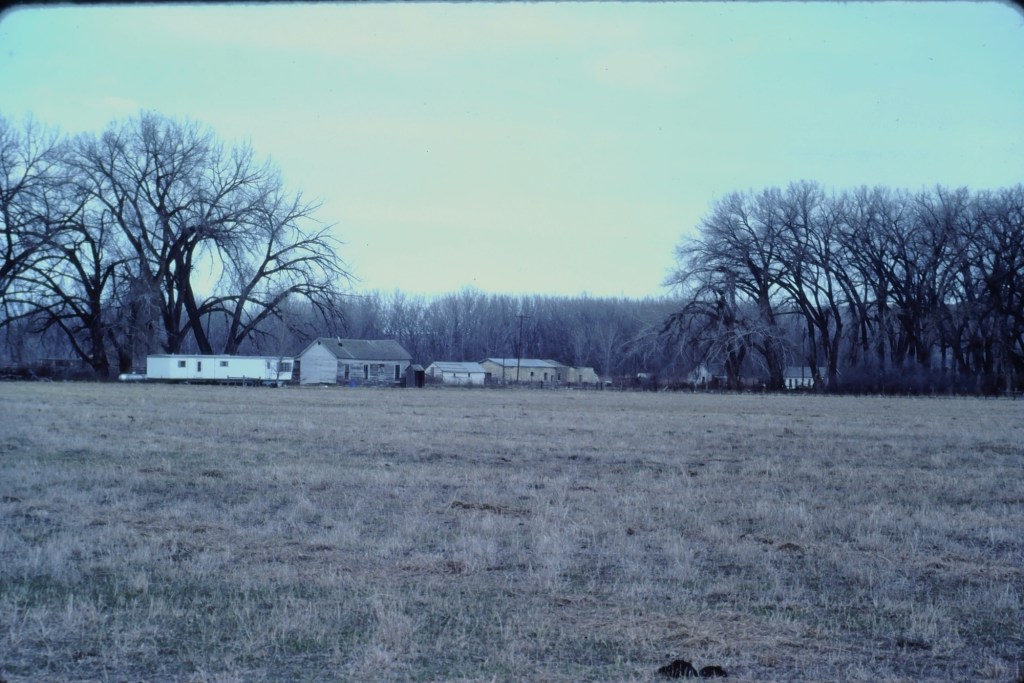

Visiting this place was a major goal of the 1984 historic preservation plan survey. At that time the ranch was still operating as a ranch and the one slide that I took shows several of the historic and new ranch buildings, yes from a distance because in the work I always respected private property boundaries.
Over the next 40 years I worked in Montana many times but never made a return to Judith Landing. I knew that the historic buildings of the PN ranch were there and that a National Register district existed affording some protection. Then in late 2024 came the news that Montana State Parks was acquiring 109 acres of the historic property and would create the Judith Landing State Park. I couldn’t wait to return and visited in late September 2025.
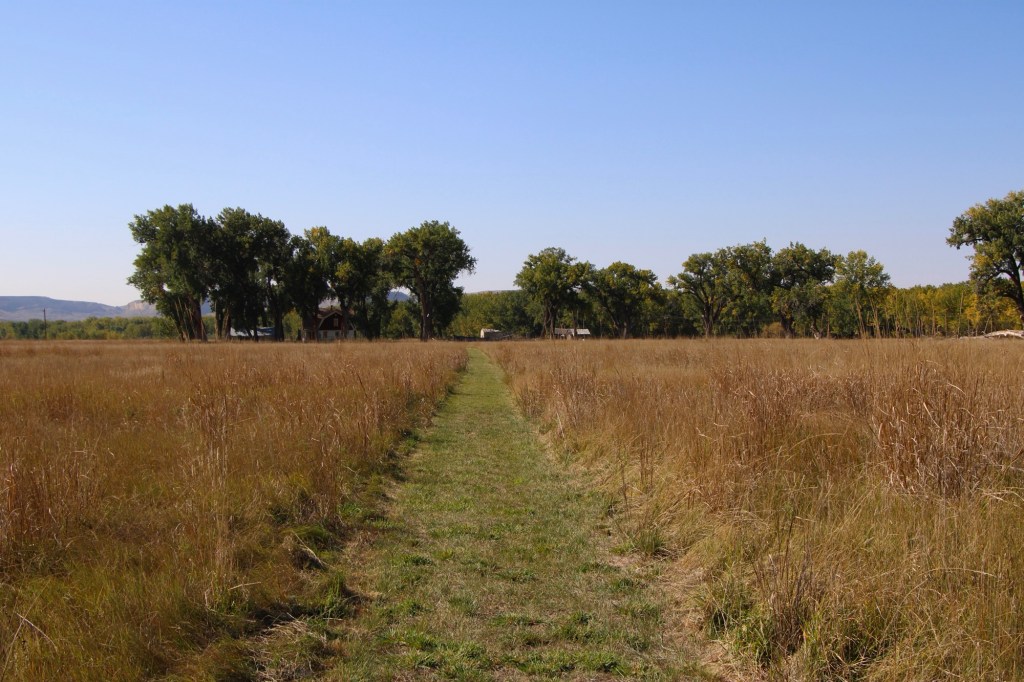


At that time there had been little in the way of “park development.” I hope it largely stays that way because the sense of time and place conveyed by the rustic, rugged surroundings is overwhelming. You can be lost in history.
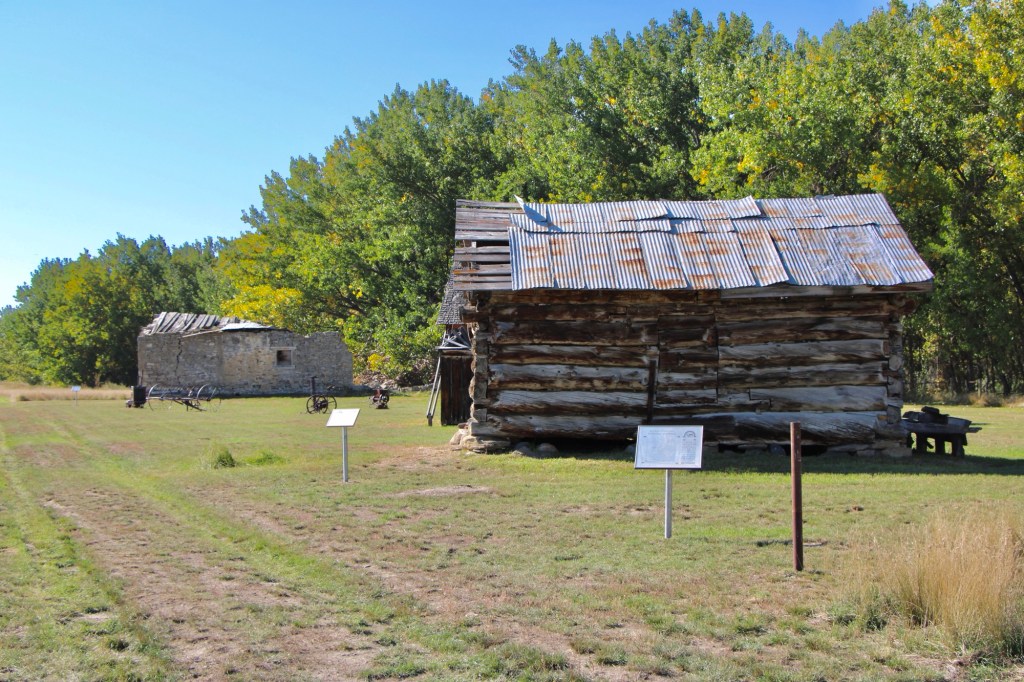

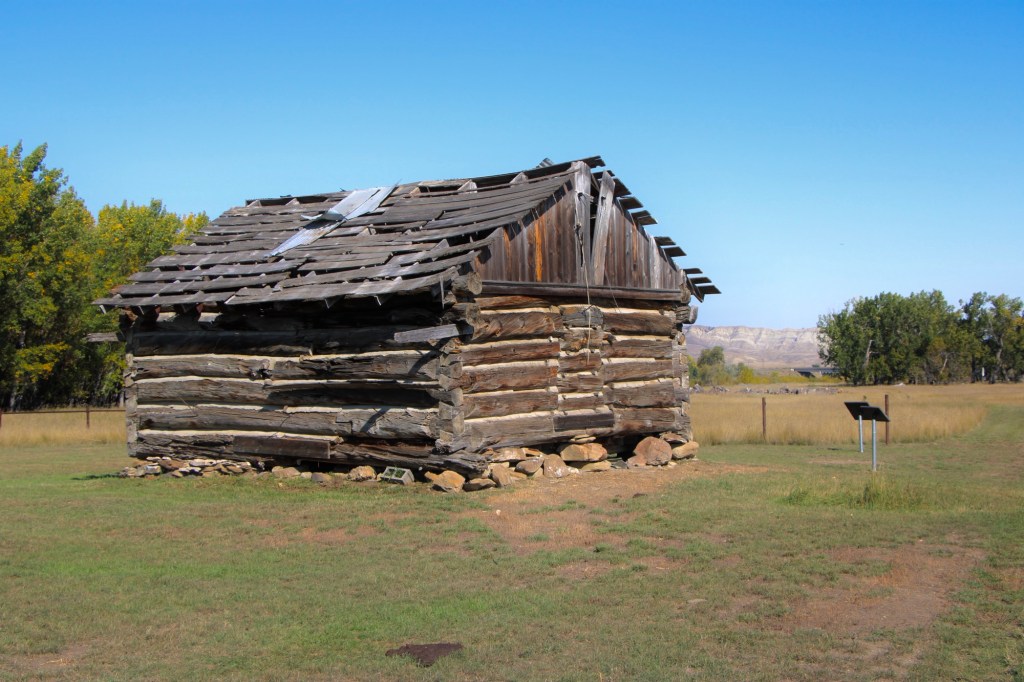
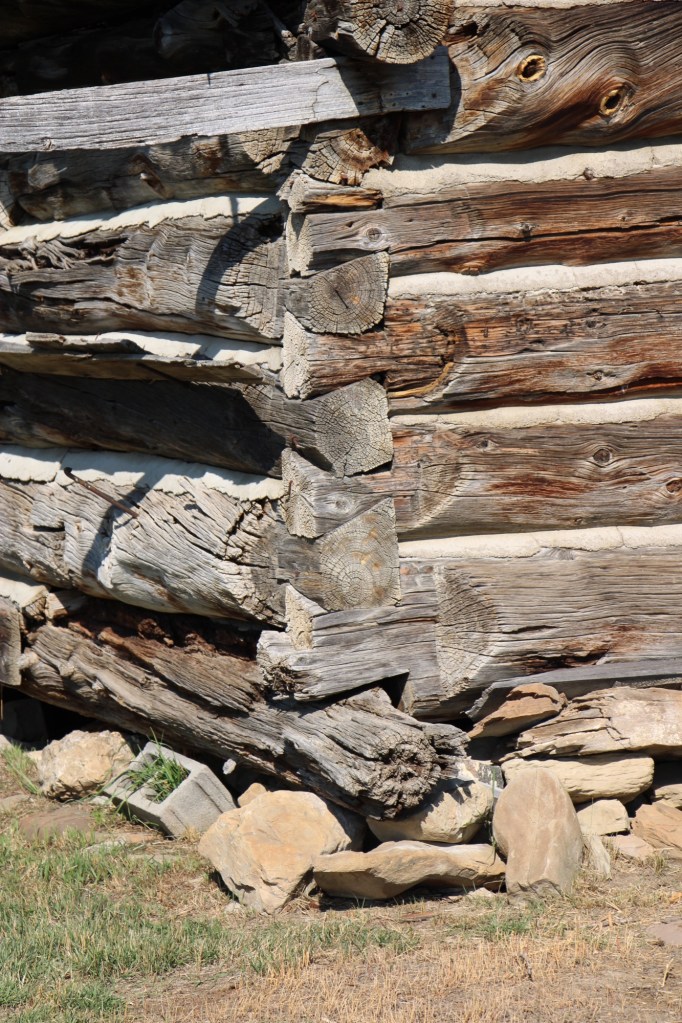
The half-dovetail “mail barn” was moved to its location on the ranch about 1890. It continued to serve as a post office until 1919.


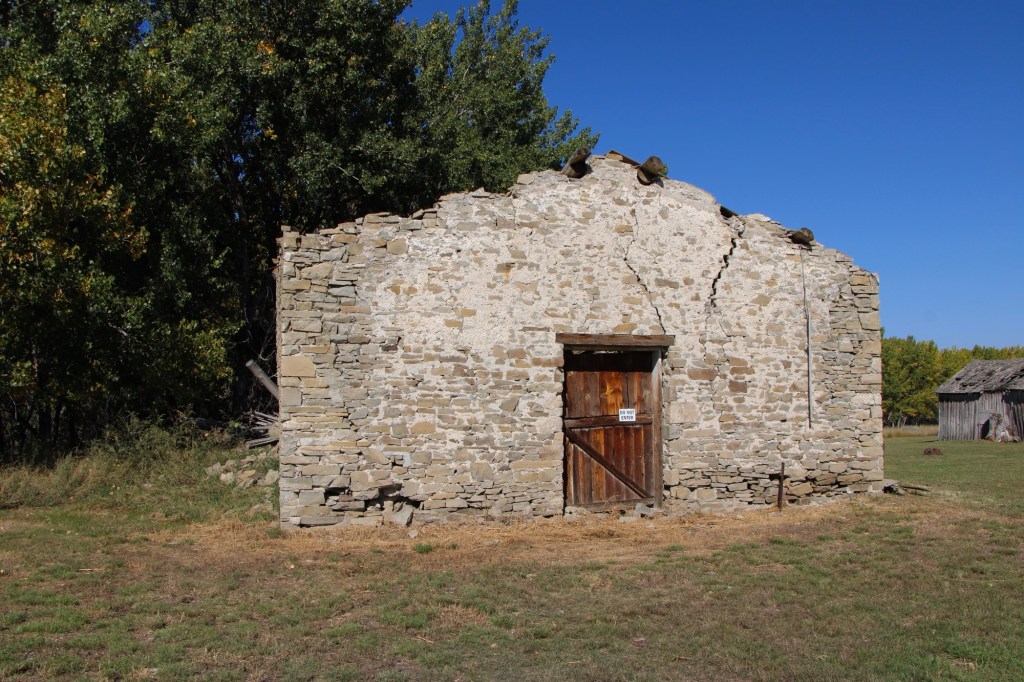
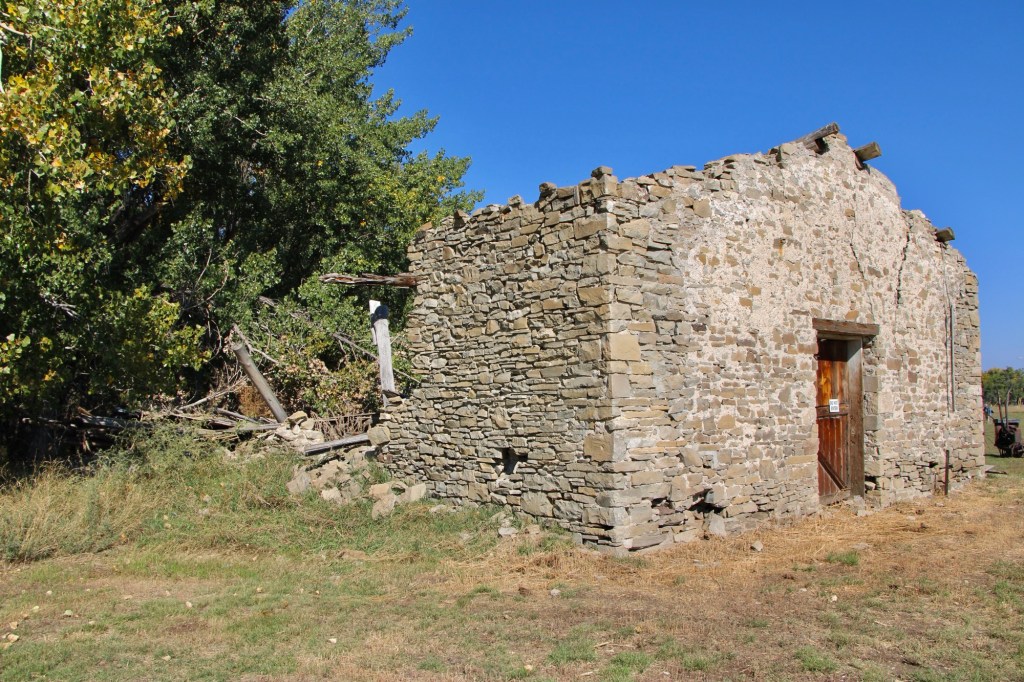
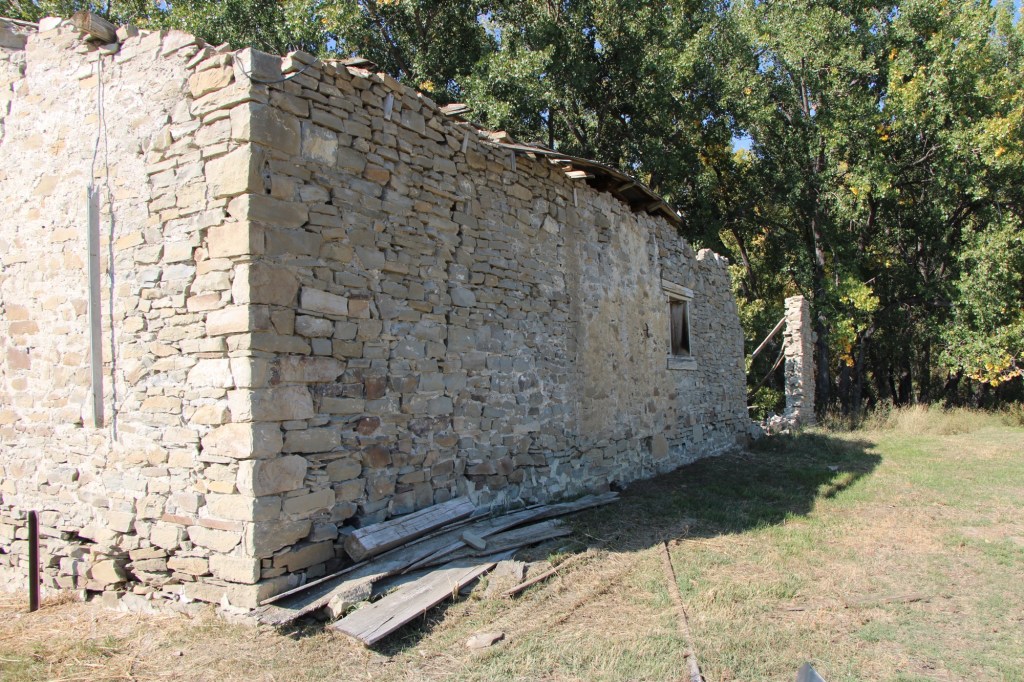
The stone warehouse was severely damaged in a flood 50 years ago—but it is hanging on, and indicates how important trade and commodities were here 150 years ago. It operated as a store until 1934 and then became a barn for the next 40 years until the flood of 1975.



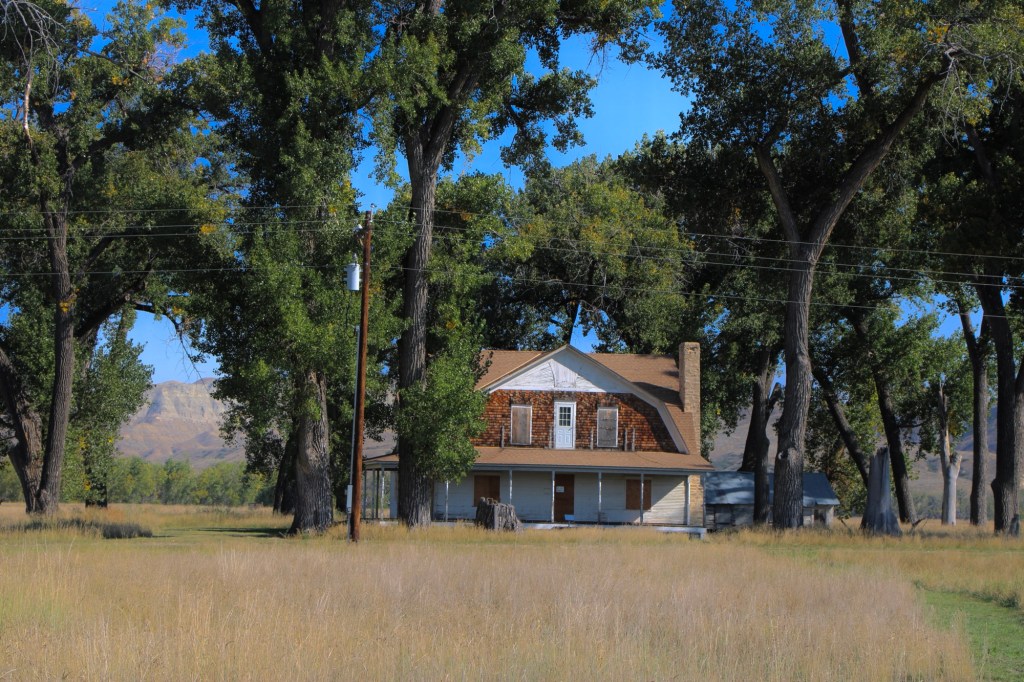
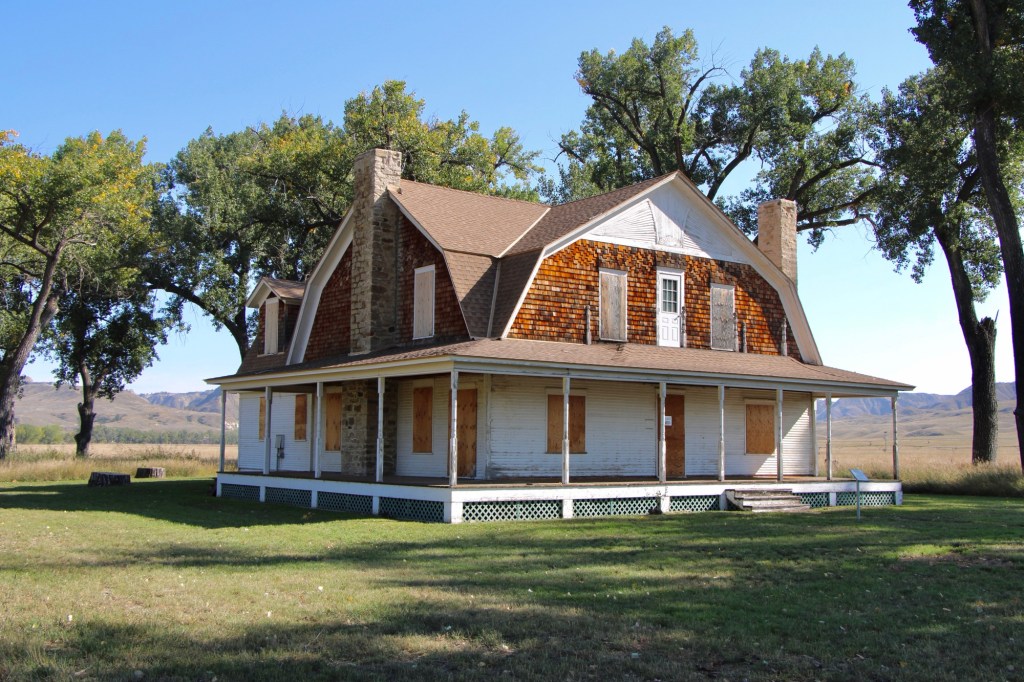
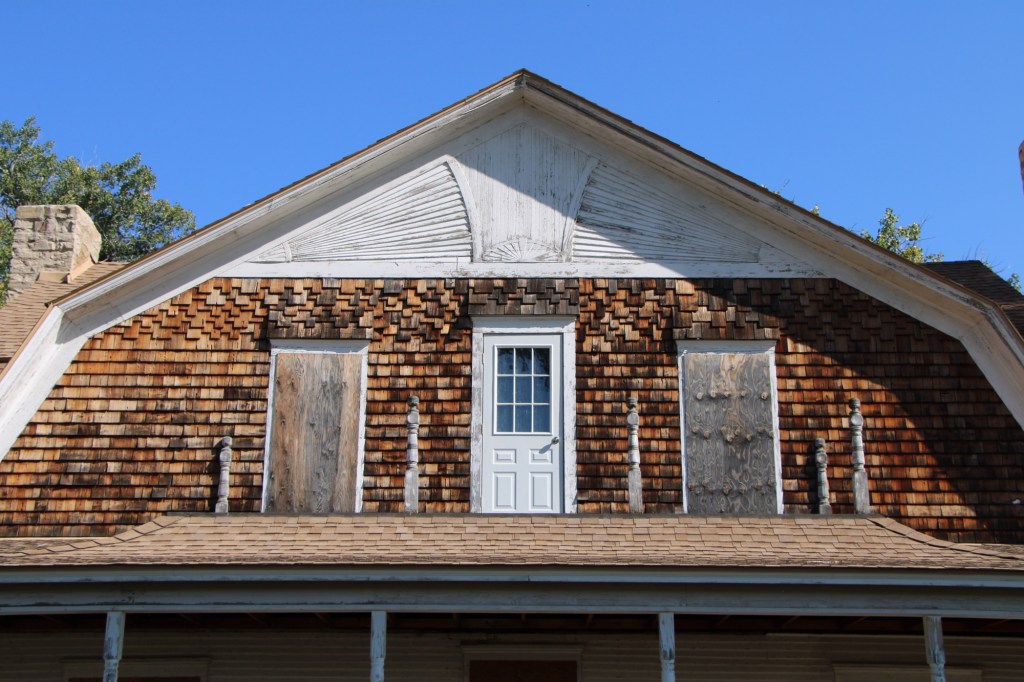
Gilman and Pauline Norris’s own ranch house, a turn of the twentieth century Shingle-style beauty, speaks to the ranch’s success. perhaps it can be restored as a future park interpretive center, open in the summer.




The important point is that, now, finally, Judith Landing is a state park, conserving one of the most remarkable places of the northern plains.